June 6, 2022
Site Selection Problem Based on Greedy Algorithm
——China MatherCup Mathematical Modeling Competition
Completed in collaboration with Jiasheng Xu and Jiangsheng Zhu
About the process
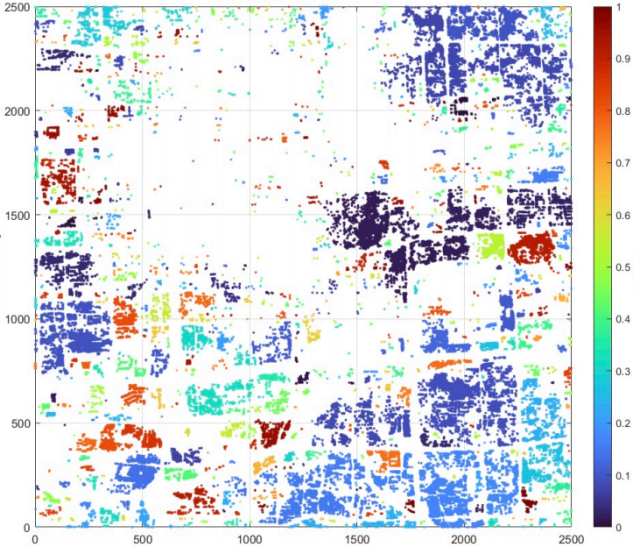
Figure: Dbscan Cluster result
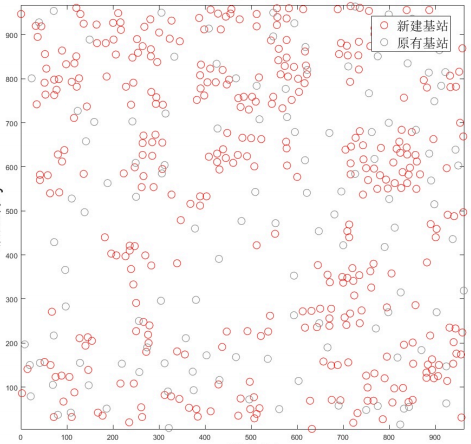
Figure: New base station location coverage map
Abstract
With the development of 5G, the variety of base stations and antennas increases, making the site selection problem more complex. By analyzing the information of given sites and weak coverage points, we established a mathematical model based on the Greedy Algorithm and the DBSCAN clustering algorithm. This model offers a solution to cover weak coverage areas in the existing network, providing optimal site selection and a regional clustering plan for weak coverage points.
For Problem 1, we established an optimal site selection model. Using the Greedy Algorithm, we selected the point with the highest uncaptured business volume as the reference for base station site selection. By comparing the total business volume covered by potential sites around this point, we chose the one covering the largest volume. This process was repeated to find the local maximum coverage volume. After multiple iterations, we determined the optimal site selection model and calculated that 2,464 new base stations are needed.
For Problem 2, we developed a Petal Rotation Model. Considering the base station coverage shape as a petal model, while applying the Greedy Algorithm, we exhaustively rotated the model 120 times using an exhaustive algorithm to find the angle at which each base station covers the maximum business volume. This process determined the local maximum coverage volume. Ensuring the number of sites was consistent with Model 1, the coverage volume accounted for 85.879% of the total business volume.
For Problem 3, we compared the K-means and DBSCAN algorithms and ultimately chose the DBSCAN clustering algorithm. Considering ε as 20 and minPts as 1, we clustered the weak coverage areas into 898 categories, including isolated points.
The models established in this paper are simple, easy to implement, and extendable. After thorough analysis and verification, they are found to be reasonable and have significant practical implications.
Keywords: Base Station Site Selection; Greedy Algorithm; Petal Model; DBSCAN Clustering Algorithm.
You could download this paper.
